Table of Contents
Understanding the Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, also known as the H-R diagram, was named after Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, two astronomers who independently developed this graphical representation in the early 1900s. The diagram plots the luminosity of stars against their temperature. Let’s delve deeper into the details.
An Overview of Figure 10.12
Figure 10.12 illustrates the luminosity and temperature data for several prominent stars. The vertical axis represents the luminosity scale, extending from 10-4 to 104 solar luminosities (3.9 x 1026 W). Interestingly, the Sun sits right in the middle of this range, with a luminosity of one. On the horizontal axis, the temperature is depicted unconventionally, increasing towards the left. Therefore, the spectral sequence O, B, A is read from left to right.

Figure 10.12: H-R Diagram of Well-Known Stars
The image above showcases the H-R diagram for the mentioned stars, providing insights into their luminosity and surface temperature. For example, our Sun, classified as a G-type star, has a temperature of 5800 K.
The Main Sequence
As Hertzsprung and Russell expanded their observations, they discovered an intriguing pattern on the H-R diagram. Stars were not randomly scattered across the plot but rather concentrated in a distinct band. This prominent band, stretching diagonally from the top left (high-temperature, high-luminosity) to the bottom right (low-temperature, low-luminosity), is referred to as the main sequence. Most stars, including those in the solar neighborhood, can be found within this region.
Shedding Light on Stellar Properties
The main sequence encompasses stars with a surface temperature ranging from approximately 3000 K (spectral class M) to over 30,000 K (spectral class O). Despite the relatively small temperature range (a factor of 10), the luminosity varies extensively, spanning eight orders of magnitude (a factor of 100 million). This colossal range covers luminosity values from 10-4 to 104 times that of the Sun.

Figure 10.13: H-R Diagram of Nearby Stars
Figure 10.13 exhibits an H-R diagram for stars situated within 5 parsecs of the Sun. It becomes apparent that most stars in the solar neighborhood align with the main sequence. The shaded region represents the area within which the majority of stars reside.
Stellar Radii and Relationships
On the main sequence, stellar radii also display variability. Red M-type stars located at the bottom right of the H-R diagram, for instance, are approximately one-tenth the size of the Sun. In contrast, blue O-type stars found in the upper left are roughly ten times larger than our Sun. To depict stellar temperatures, luminosities, and radii simultaneously, dashed lines indicating constant stellar radii are incorporated into the H-R diagrams.
Hence, the relationship between radius, luminosity, and temperature can be expressed as follows:
Luminosity µ Temperature^4.
With this additional information, astronomers can gain a comprehensive understanding of stellar properties from a single diagram.
The Stars in the Main Sequence
At the central point of the main sequence resides our Sun. As we move towards the upper end of the sequence, stars grow larger, hotter, and more luminous. These colossal stars are known as blue giants, with the largest among them labeled as blue supergiants. Conversely, stars situated at the opposite end of the main sequence are smaller, cooler, and less luminous. These stars, referred to as red dwarfs, are the most abundant in the universe.
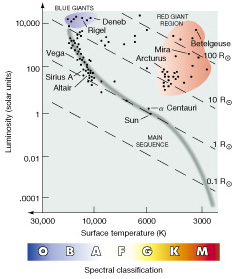
Figure 10.14: H-R Diagram of Brightest Stars
Figure 10.14 provides an H-R diagram illustrating the 100 brightest stars visible from Earth. Here, we observe a prevalence of stars at the upper section of the main sequence. This overrepresentation of blue giants is attributed to their significant luminosity, enabling us to observe them from great distances. It is noteworthy that this sample includes stars scattered across a much larger volume of space compared to the stars in Figure 10.13. As a result, the most luminous objects dominate this diagram.
The White-Dwarf and Red-Giant Regions
While the majority of stars fall onto the main sequence, some data points in Figures 10.12 to 10.14 deviate from this pattern. For instance, Sirius B, represented as a point in Figure 10.12, represents a white dwarf. Despite having a surface temperature four times higher than that of the Sun, its luminosity is only 0.04 times that of our star. Additional faint bluish-white stars, located in the bottom left-hand corner of Figure 10.13, also reside outside the main sequence in the white-dwarf region.
Another noteworthy presence is Mira, featured in Figure 10.12. With half the surface temperature of the Sun (3000 K), Mira’s luminosity surpasses 400 times that of our star. Similarly, Betelgeuse, the ninth brightest star in the sky, appears hotter than Mira and emits over 30 times more luminosity. These stars, along with others in the upper right-hand corner of the H-R diagram, classify as red giants or supergiants. Although red giants do not exist within 5 parsecs of the Sun (as demonstrated in Figure 10.13), they populate the sky as some of the brightest stars (visualized in Figure 10.14). These red giants constitute a distinct class of stars, significantly varying from both main-sequence stars and white dwarfs.


